Cumulative Dividend Definition, Formula, How to Calculate?
And then, the firm will pay the accumulated preferred dividends to the preferred shareholders. This feature of arrear payment is only available with the cumulative preferred stock. And the firm is legally obligated to pay off the previous year’s preferred dividend before paying the current year’s dividend. It means that if you’re a preferred shareholder, you will get a fixed percentage of dividends every year. And the most valuable part of the preferred stock is that the preferred shareholders get a higher dividend rate.
- Please read the SEBI prescribed Combined Risk Disclosure Document prior to investing.
- Since the dividend is always paid in cash, its shortage will force the company to withhold dividend payments for 2016.
- This feature gives investors flexibility, allowing them to lock in the fixed return from the preferred dividends and, potentially, to participate in the capital appreciation of the common stock.
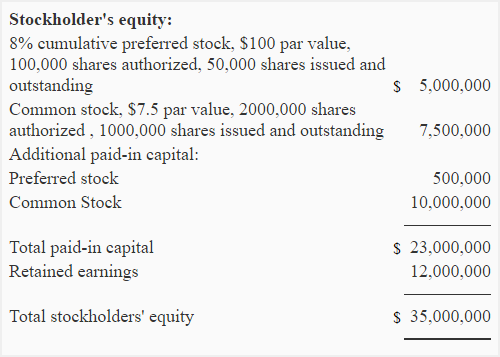
- Cumulative preferred stock is one type of preferred stock; a preferred stock typically has a fixed dividend yield based on the par value of the stock.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
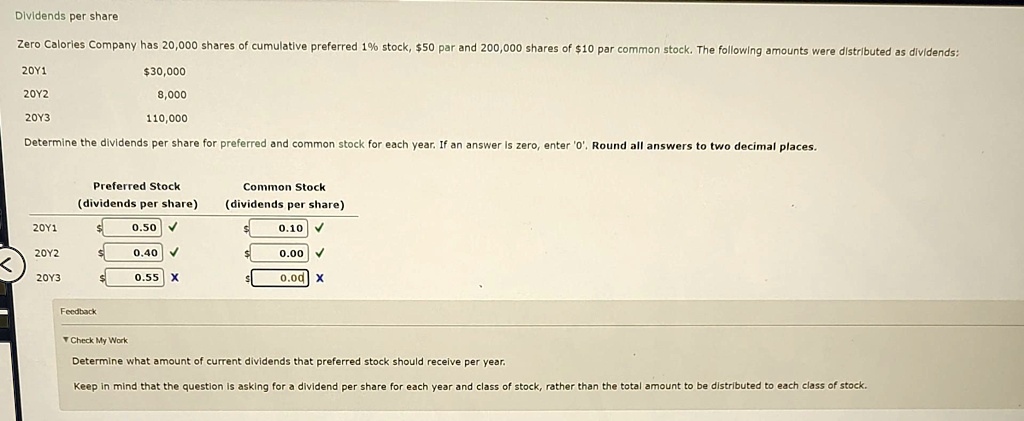
If your preferred stock dividends are suspended, here’s how to figure out how much you’re owed. Therefore, the numerator is not adjusted for the preferred dividends that are actually paid during the part of the year in which they were outstanding. For fully diluted EPS, conversion is assumed for all preferred shares that are convertible within the next 10 years. Preferred shares are anti-dilutive if the dividends saved per issuable common share exceed EPS without assuming conversion.
Common features of preferred dividend
Due to this lower cost of capital, most companies’ preferred stock offerings are issued with the cumulative feature. Generally, only blue-chip companies with strong dividend histories can issue non-cumulative preferred stock without increasing the cost of capital. The cumulative preferred stock shareholders must be paid the $900 in arrears in addition to the current dividend of $600. Once all cumulative shareholders receive the $1,500 due per share, the company may consider paying dividends to other classes of shareholders. Conversions and issuances during a reporting period will have an impact on eps if it is assumed that they were in place for the entirety of the year. To determine the number of issue shares attributable to this, calculate earnings per share (eps) for the part of the year in which the convertible preferred stock was not outstanding.
Video Explanation of Preferred Dividend
However, the relative move of preferred yields is usually less dramatic than that of bonds. Preferred dividends referred to the amount of dividend payable on the company’s preferred stock from the profits earned by the company. Preferred dividends are issued based on the par value and dividend rate of the preferred stock. While preferred dividends are issued at a fixed rate based on their par value, this may be unfavorable in high inflation periods. This is because the fixed payment is based on a real rate of interest and is typically unadjusted for inflation.
Dividend Payment Hierarchy
The fixed, consistent coupon rate of preferred dividends provides a stability that common dividends may lack. You can calculate your preferred stock’s annual dividend distribution per share by multiplying the dividend rate and the par value. The dividend rate multiplied by the par value equals the total annual preferred dividend. If it is paid out in installments, such as in quarters, the issuer divides the total preferred dividend by the number of periods to get an approximate installment payment. The boards of directors of public companies determine whether to pay a dividend to holders of its common stock and how much to pay out.
How to Calculate Dividend Distribution of Preferred Stocks
If a company cannot pay all of its dividends, it must pay preferred dividends before paying dividends to holders of common stock. If a company’s earnings go up, the company may increase the dividend rate it pays to common stock shareholders. Dividend payments to common shareholders, in general, tend to go up over time. However, for most preferred shareholders, who own non-participating stock, the dividend rate will always remain the same.
A company that issues preferred shares commits to paying a specified dividend amount. Preferred dividends are the dividends that are accrued paid on a company’s preferred the 10 best tax preparation services in baltimore, md 2021 stock. If the company is unable to pay all the dividends, then claims to any preferred dividends will take precedence over claims to dividends on common shares.
Investors often seek preferred stocks for their consistent returns and diversification benefits. To fully understand the nuances of preferred dividends and their strategic role in an investment portfolio, continue exploring the details. In contrast, holders of the cumulative preferred stock shares will receive all dividend payments in arrears before preferred stockholders receive a payment.
