Notes receivable accounting
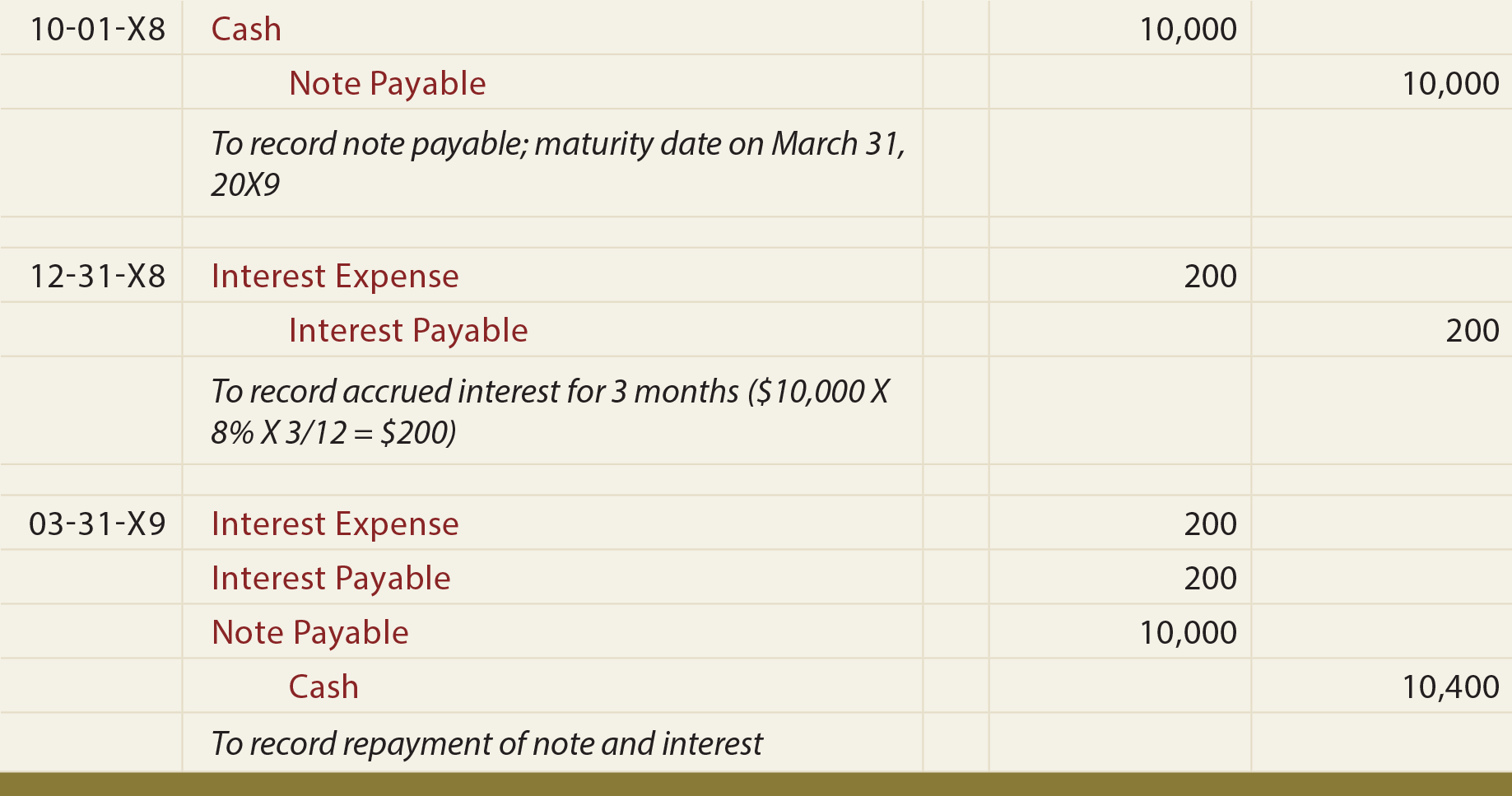
On January 1, 2018, Waterways purchased merchandise in the amount of $250,000. BWW agreed to lend the $250,000 purchase cost (sales price) to Waterways under the following conditions. The conditions of the note are that the principal amount is $250,000, the maturity date on the note is 24 months, and the annual interest rate is 12%. Notes receivable have several defining characteristics that include principal, length of contract terms, and interest. The principal of a note is the initial loan amount, not including interest, requested by the customer. If a customer approaches a lender, requesting $2,000, this amount is the principal.
Time Value of Money
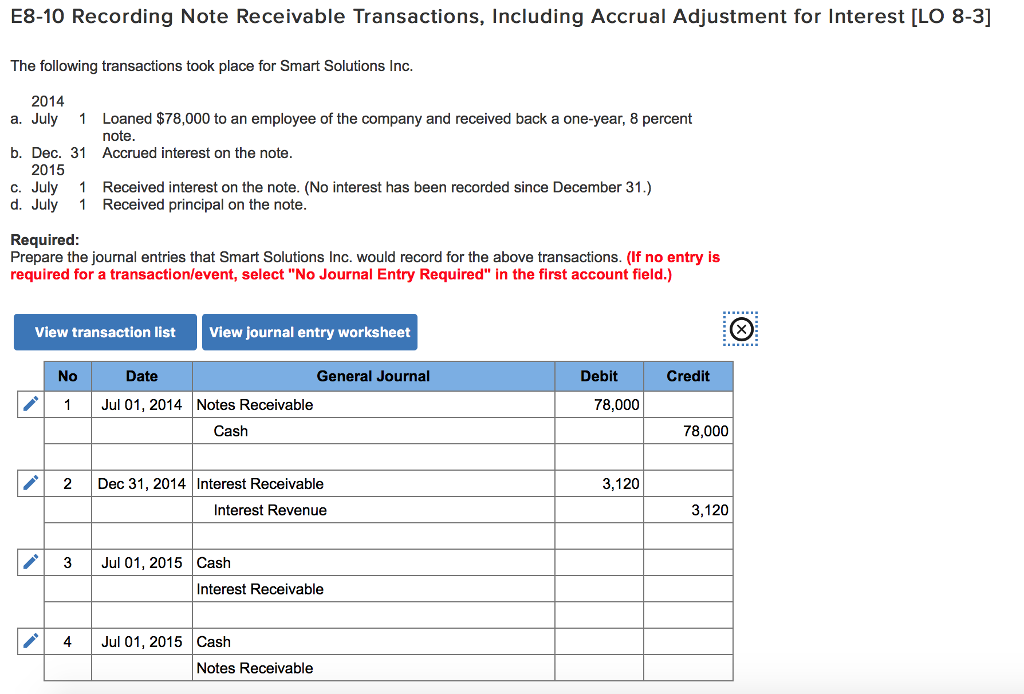
As at 31 December, the note receivable from ABC is classified as a non-current asset because it is due after 12 months from 31 December. Interest receivable on the note as a 31 December is reported as current asset because it is to be received at the end of April 20X5. The amount debited to notes receivable represent the interest earned in month of December on the carrying amount at the end of November because the note carries compound interest.
- This period of time is important in calculating the interest charges related to the notes.
- The principal of a note is the initial loan amount, not including interest, requested by the customer.
- Also, the company may be able to sell the note to a bank or other financial institution.
- Interest revenue from year one had already been recorded in 2018, but the interest revenue from 2019 is not recorded until the end of the note term.
Accounting Ratios
When notes receivable have terms of less than one year, accounting for short-term notes is relatively straight forward as discussed below. Record the conversion of the account receivable balance to note receivable. Among these, one customer with a $5,000 wants to convert the balance to a note receivable. A note receivable also comes with a predetermined interest rate after a mutual agreement between both parties.
Journal entry for non interest bearing note receivable
Periodic interest accrued is recorded in Interest Revenue and Interest Receivable. The following example uses months but the calculation could also be based on a 365-day year. Notes receivable are assets and represent amounts due to a business by a third party (usually a customer).
Determine the Present Value (PV) of Future Cash Flows, to record the Note Receivable at its Fair Value. In some instances, an Accounts Receivable amount may be changed to a Note Receivable by agreement between the company and the customer. This is usually done to give the company a more formal agreement with a customer with an overdue balance. Assume if RSP was unable to pay the final installment of USD20,000 and the related interest of USD165 and MPC has been accruing this interest income. MPC has to write off the remaining balance of the note with interest due. Now the note has been completely discharged, MPC has recorded an interest income of USD987.
What is the Difference Between a Note Receivable and a Note Payable?
Terrance Inc. agrees to grant Dino-Kleen a longer period of time to pay the invoice in exchange for 5% interest. This means the interest on the note is earned in the January, February, March, and April accounting periods. To record a note receivable, you will need to debit the cash account and credit the notes receivable account.
Furthermore, by transferring the note to Accounts Receivable, the remaining balance in the notes receivable general ledger contains only the amounts of notes that have not yet matured. When the payment on a note is received, Cash is debited, Note Receivables is credited, and Interest Revenue is credited. When a note is received from a customer, the Notes Receivable account is debited.
No interest receivable account is used when the note carries compound interest, because in that case the carrying amount of notes receivable is increased by debiting it, as seen above. However, if any note is repayable after a year, companies must qualify it as non-current assets. A company should evaluate all its note receivables for classification at each reporting date. To show the initial recording of notes receivable, assume that on 1 July, the Fenton Company accepts a $2,000, 12%, 4-month note receivable from the Zoe Company in settlement of an open account receivable. Other notes receivable result from cash loans to employees, stockholders, customers, or others. By the time the non-interest-bearing note is honored, its balance will already equal to its face value written on the promissory note.
What distinguishes notes receivables from accounts receivable is that they are issued as a promissory note (a formal legal agreement given as a written note promising to pay principal plus interest at a specific date). However, for any receivables due in less than one year, this interest income component is usually insignificant. For this reason, both IFRS and ASPE allow net realizable value (the net amount expected to be received in cash) to approximate the fair value for short-term notes receivables that mature within one year. However, for notes with maturity dates greater than one year, fair values are to be determined at their discounted cash flow or present value, which will be discussed next. A written promise from a client or customer to pay a definite amount of money on a specific future date is called a note receivable.
When a customer does not pay an account receivable that is due, the company may insist that the customer gives a note in place of the account receivable. Notes receivables describe promissory notes that represent loans paid from a company or business to another party. The note comes with a promise from the borrower that it operating profit vs net income will repay the lender in the future. BWW issued Sea Ferries a note in the amount of $100,000 on January 1, 2018, with a maturity date of six months, at a 10% annual interest rate. On July 2, BWW determined that Sea Ferries dishonored its note and recorded the following entry to convert this debt into accounts receivable.
