Operating Expense OpEx Definition and Examples
Content

Raw materials are the direct goods purchased that are eventually turned into a final product. If the athletic brand doesn’t make the shoes, it won’t incur the cost of leather, synthetic mesh, canvas, or other raw materials. In general, a company should spend roughly the same amount on raw materials for every unit produced assuming no major differences in manufacturing one unit versus another. CapEx includes major expenses like patents and buying office space while OpEx includes recurring expenses like staff salaries and machine upkeep. Both these types of expenses are important to keep a business functional and growing. Variable expenses depend on output and production changes, meaning they fluctuate depending on how much you’re using.
Variable costs are commonly designated as COGS, whereas fixed costs are not usually included in COGS. Fluctuations in sales and production levels can affect variable costs if factors such as sales commissions are included in per-unit production costs. Meanwhile, fixed costs must still be paid even if production slows down significantly. A company that seeks to increase its profit by decreasing variable costs may need to cut down on fluctuating costs for raw materials, direct labor, and advertising. However, the cost cut should not affect product or service quality as this would have an adverse effect on sales. By reducing its variable costs, a business increases its gross profit margin or contribution margin.
Operating Expenses: Overview, Definition and Examples
Variable costs increase or decrease depending on a company’s production or sales volume—they rise as production increases and fall as production decreases. By keeping track of the variable expense to gross income ratio, a landlord can determine if variable operating expenses variable expenses are increasing above their historical rate. Let’s change the example and say that there are only five tenants occupying five floors. Now, the total janitorial expenses would be only $5,000 ($1,000 per floor for five floors).
- However, anything above this has limitless potential for yielding benefit for the company.
- Thus, your company’s revenue is the first item that appears on the income statement.
- Therefore, the cost of shipping a finished good varies (i.e. is variable) depending on the quantity of units shipped.
- Purchasing machinery, for example, is considered a capital expenditure, whereas, repair and maintenance of the machinery is considered an operating expense.
- Therefore, Amy would actually lose more money ($1,700 per month) if she were to discontinue the business altogether.
Variable costs are a direct input in the calculation of contribution margin, the amount of proceeds a company collects after using sale proceeds to cover variable costs. Every dollar of contribution margin goes directly to paying for fixed costs; once all fixed costs have been paid for, every dollar of contribution margin contributes to profit. In general, companies with a high proportion of variable costs relative to fixed costs are considered to be less volatile, as their profits are more dependent on the success of their sales.
Utilities
The marginal cost will take into account the total cost of production, including both fixed and variable costs. Since fixed costs are static, however, the weight of fixed costs will decline as production scales up. If companies ramp up production to meet demand, their variable costs will increase as well. If these costs increase at a rate that exceeds the profits generated from new units produced, it may not make sense to expand. A company in such a case will need to evaluate why it cannot achieve economies of scale. In economies of scale, variable costs as a percentage of overall cost per unit decrease as the scale of production ramps up.
If you budget by paycheck or schedule automatic bill payments, having bills due at roughly the same time can help with avoiding late payments and the fees that go along with them. When making a budget, it’s important to know how to separate fixed expenses from variable expenses. This is because it seems an easy and approachable way of increasing your business profits.
AccountingTools
Her work has also been featured in scores of publications and media outlets including Business Insider, Chicago Tribune, The Independent, and Digital Privacy News. It’s important not only that you have a budget but also that you make an effort to live your budget. This means that you go beyond simply planning out your budget and commit to the spending rules you’ve laid down for yourself. Living your budget may mean rethinking wants versus needs to avoid overspending.
- Calculating and controlling operating expenses is crucial for small and medium-sized companies to remain operational.
- The IRS has guidelines related to how businesses must capitalize assets, and there are different classes for different types of assets.
- A company that seeks to increase its profit by decreasing variable costs may need to cut down on fluctuating costs for raw materials, direct labor, and advertising.
- They are essential to the income statement, reflecting the costs incurred to sustain day-to-day operations and generate revenue.
- A fixed cost is one that does not change with an increase or decrease in sales or productivity and must be paid regardless of the company’s activity or performance.
A fixed cost remains the same no matter what the production level is, while variable cost does vary with the number of products or services that a company produces. Along with operating expenses, overhead costs are subtracted from the gross income to arrive at the net income figure, which shows business owners the company’s profitability. In today’s competitive business landscape, understanding and managing operating expenses is crucial for a company’s financial success and sustainability. They are essential to the income statement, reflecting the costs incurred to sustain day-to-day operations and generate revenue. Operating expenses are any costs that a business incurs in its day-to-day business.
Rent and lease payments refer to the cost of renting or leasing office space, equipment, or other assets needed for business operations. Effectively managing operating expenses is a critical component of maintaining strong financial health and ensuring the long-term success of any business. SG&A includes nearly everything that isn’t in the cost of goods sold (COGS). For example, the fast-food company may buy its potatoes at $0.50 per pound when it buys potatoes in amounts of less than 200 pounds. However, the potato supplier may offer the restaurant chain a price of $0.45 per pound when it buys potatoes in bulk amounts of 200 to 500 pounds.
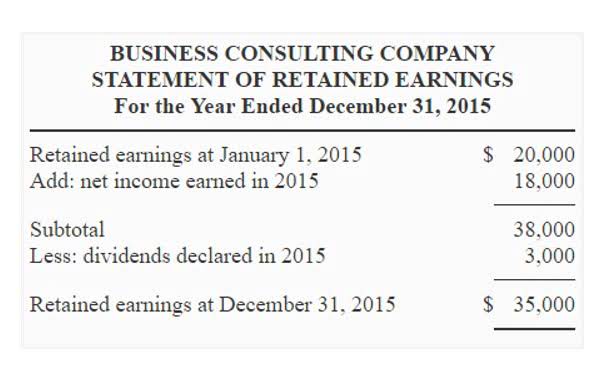
A non-operating expense is a cost that is unrelated to the business’s core operations. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows businesses to deduct operating expenses if the business operates to earn profits. However, the IRS and most accounting principles distinguish between operating expenses and capital expenditures. Operating expenses are the costs that a company incurs while performing its normal operational activities. Operational activities are those tasks that must be undertaken from day to day to operate the business and generate revenue. Operating expenses are different from expenses relating to, for example, investing in projects and borrowing.
